Bitcoin’s Blockchain Work: The first decentralized cryptocurrency to be designed, Bitcoin, utilizes a novel blockchain technology. This digital ledger system is paramount for creating trust, security, and immutability, therefore allowing Bitcoin to function as a trustless and peer-to-peer payment network. In addition, how does the functioning of the Bitcoin blockchain work?
Well, we shall try to unravel how the Bitcoin blockchain works, transaction validation, the mining process, and security features. In addition, you shall see why blockchain is seen as one of the most revolutionary innovations in finance and technology.
1. What Is a Blockchain?
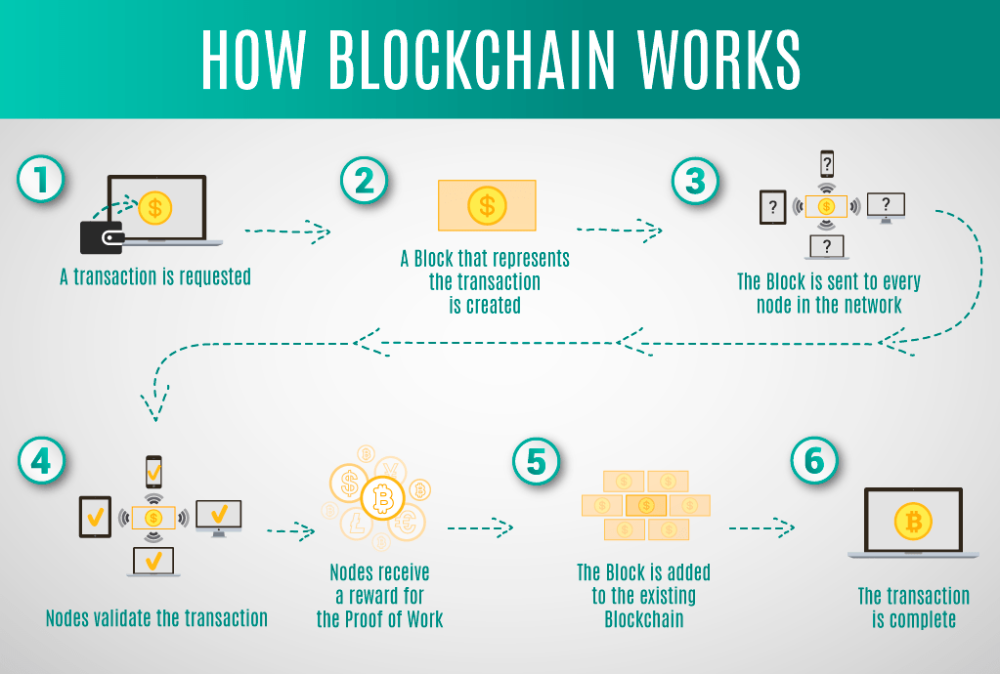
A blockchain is a distributed ledger that records transactions across a network of computers (nodes). Unlike banking systems in which there is a known authority that keeps the records, Bitcoin’s blockchain is decentralized, meaning that it is not controlled and governed by a single entity.
Key characteristics of Bitcoin’s Blockchain:
- Decentralization: Operated across a global network of nodes.
- Immutability: Transactions cannot be altered once recorded.
- Transparency: All transactions can be verified publicly.
- Security: Cryptographic techniques are applied to prevent forgery.
2. The Structure of Bitcoin’s Blockchain
Bitcoin’s blockchain consists of a series of blocks linked together chronologically. Each block contains:
A. Transaction Data
- A list of verified Bitcoin transactions (sender, receiver, amount).
- Transactions are grouped into blocks (each block holds around 1MB–4MB of data).
B. Block Header
- Previous Block Hash: A unique fingerprint of the previous block, creating the “chain.”
- Timestamp: When the block was mined.
- Nonce: A random number used in mining (more on this later).
- Merkle Root: A cryptographic hash summarizing all transactions in the block.
This structure ensures that tampering with any transaction would require altering all subsequent blocks—a near-impossible feat due to Bitcoin’s computational security.
- How Transactions Are Verified
Before a transaction is added to the blockchain, it must go through a consensus mechanism called Proof of Work (PoW). Here’s how it works:
Transaction Submission
- A user sends Bitcoin by signing a transaction with their private key.
- The transaction is broadcast to the Bitcoin network.
Validation by Nodes
- Nodes (computers running Bitcoin software) check:
- If the sender has sufficient funds.
- If the transaction follows Bitcoin’s rules (e.g., valid signatures).
- In addition, Valid transactions enter the mempool (a waiting area for unconfirmed transactions).
Mining & Block Creation
- Miners compete to bundle transactions into a new block.
- They solve a complex cryptographic puzzle (finding a hash below a target value).
- The first miner to solve it broadcasts the new block to the network.
Block Confirmation
- In addition, other nodes verify the block’s validity.
- Once confirmed, it’s added to the blockchain.
- The miner receives a block reward (newly minted Bitcoin + transaction fees).
4. The Role of Mining in Blockchain Security
Mining is crucial for Bitcoin’s security and decentralization. Here’s why:
A. Proof of Work (PoW) Explained
- Miners use powerful computers to solve mathematical problems.
- The difficulty adjusts every 2,016 blocks (~2 weeks) to maintain a 10-minute block time.
- This process ensures that no single entity can easily dominate the network.
B. Why Mining Is Resource-Intensive
- The PoW system requires significant computational power (hash rate).
- Attackers would need 51% of the network’s hash rate to alter transactions, making Bitcoin highly secure.
C. Block Rewards & Halving
- Miners earn 6.25 BTC per block (as of 2024).
- Every 210,000 blocks (~4 years), the reward halves (the next halving in 2024 reduces it to 3.125 BTC).
- This scarcity mechanism mimics gold, ensuring Bitcoin’s value over time.
5. How Bitcoin’s Blockchain Prevents Double-Spending
Double-spending is a significant issue in digital currencies, where someone tries to spend the same Bitcoin twice. Bitcoin’s blockchain solves this by Coin E Tech – Latest News on Crypto:
A. Transaction Ordering
- In addition, once a transaction is confirmed in a block, it cannot be reversed.
- Subsequent blocks further secure it (6 confirmations are considered final).
B. Consensus Rules
- Nodes reject invalid transactions (e.g., spending nonexistent coins).
- The longest valid chain is accepted as the truth (preventing fraud).
- Challenges & Limitations of Bitcoin’s Blockchain
While Bitcoin’s blockchain is secure, it faces some challenges:
A. Scalability Issues
- Limited to 7–10 transactions per second (TPS) (vs. Visa’s ~24,000 TPS).
- Solutions like the Lightning Network enable faster, off-chain payments.
B. Energy Consumption
- PoW mining consumes significant electricity (~0.5% of global usage).
- Some argue for alternative consensus mechanisms like Proof of Stake (PoS).
C. Transaction Fees & Speed
- High demand increases fees and confirmation times.
- In addition, users can pay higher fees for faster processing.
Conclusion
Based on blockchain technology, In addition, Bitcoin provides a decentralized, secure, and transparent ledger that has altered the face of digital transactions. In addition, it corroborates the established scenario in which cryptographic methods, the Proof of Work mechanism, and peer-to-peer networking remove trust in intermediaries and prevent fraud. Scalability and energy consumption are the real challenges faced by Bitcoin, and thus there are new initiatives such as the Lightning Network that will be helping Bitcoin gain better efficiencies. In addition, understanding how blockchain operates offers real insight into the limitless potential of Bitcoin, and this potential as a currency lays the foundation for a decentralized financial future.